AMD’s new Radeon RX 6800S is said to bring maximum performance to particularly thin gaming laptops. The benchmark test in comparison with the Radeon RX 6800M shows how much performance it offers, but also reveals: not only the technology, but also the name makes the product. Gaming laptop customers should stay tuned.
AMD Mobile Radeon RX 6000 for Laptops
To date, AMD’s RDNA 2 architecture has also been available in three versions for laptops: Radeon RX 6800M, Radeon RX 6700M, and Radeon RX 6600M have been competing in a small number of gaming laptops from Asus, HP, Lenovo, and MSI. since summer 2021. of customers With the Radeon RX 6800M (test), the editors tested the top model in 2021, but it has little in common with the Radeon RX 6800 for desktop PCs: instead of Navi 21, it is based on Navi 22, much smaller.
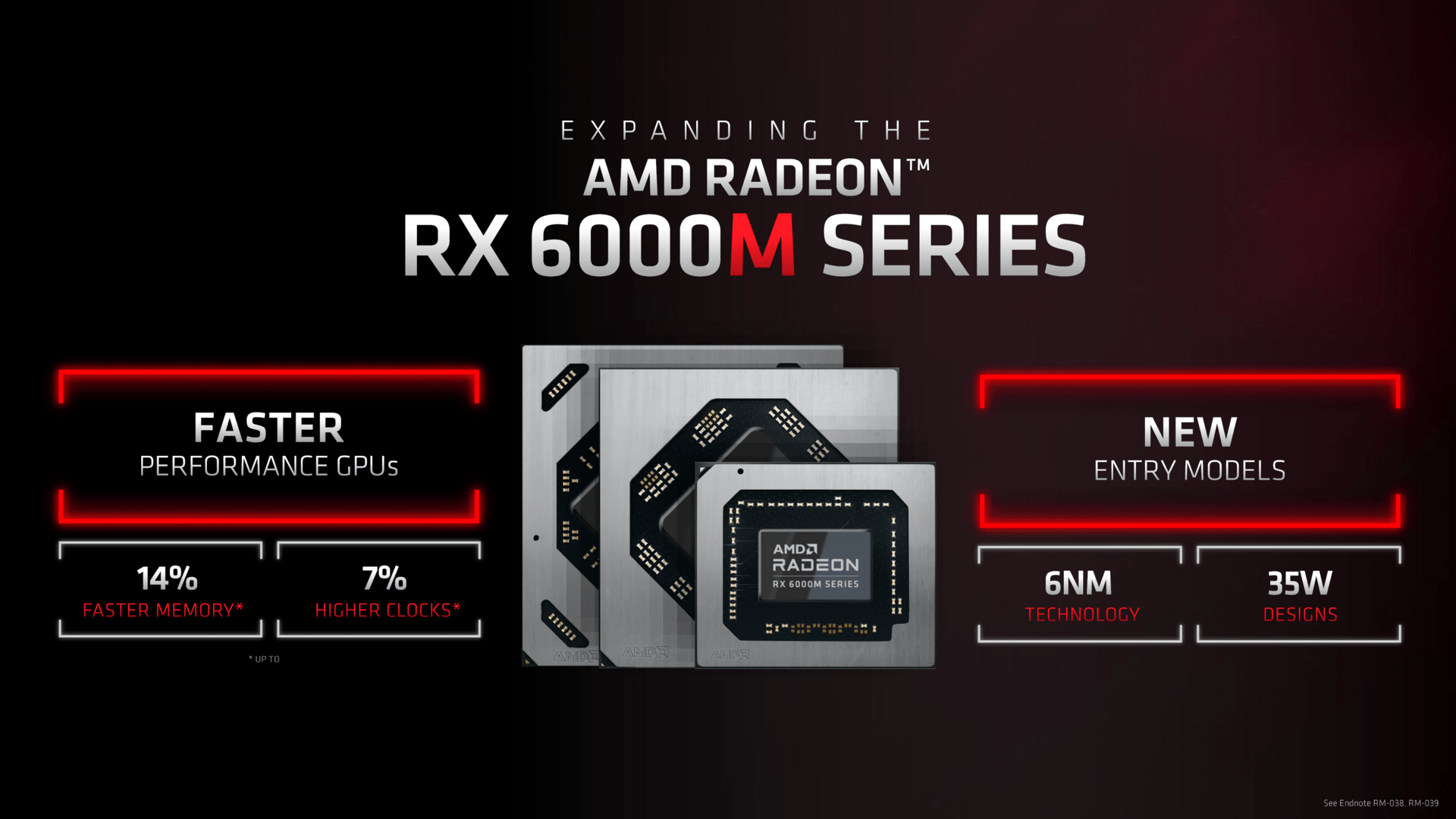
AMD has now significantly expanded the range of mobile models for CES. The new SKUs are from the M-series and three SKUs from the new S-series.
Radeon RX 6000M for “maximum performance”
At AMD, the M-series represents the “peak” performance within its class (6800, 6700, 6600, etc.). With the Radeon RX 6850M XT there is a new top model with a higher clock rate and thus more consumer. Radeon RX 6650M XT and Radeon RX 6650M are Radeon RX 6600M that have been updated with more shaders or more clocks. Radeon RX 6500 and Radeon RX 6300M are two new absolute entry-level models that use the same chip as Radeon RX 6500 XT (test) for desktop PCs: Navi 24.
The following table contains key data for existing and new models (red). The desktop PC’s Radeon RX 6700 XT is used for comparison, which, like the large mobile variants, is based on the Navi 22 chip with 40 active compute units.
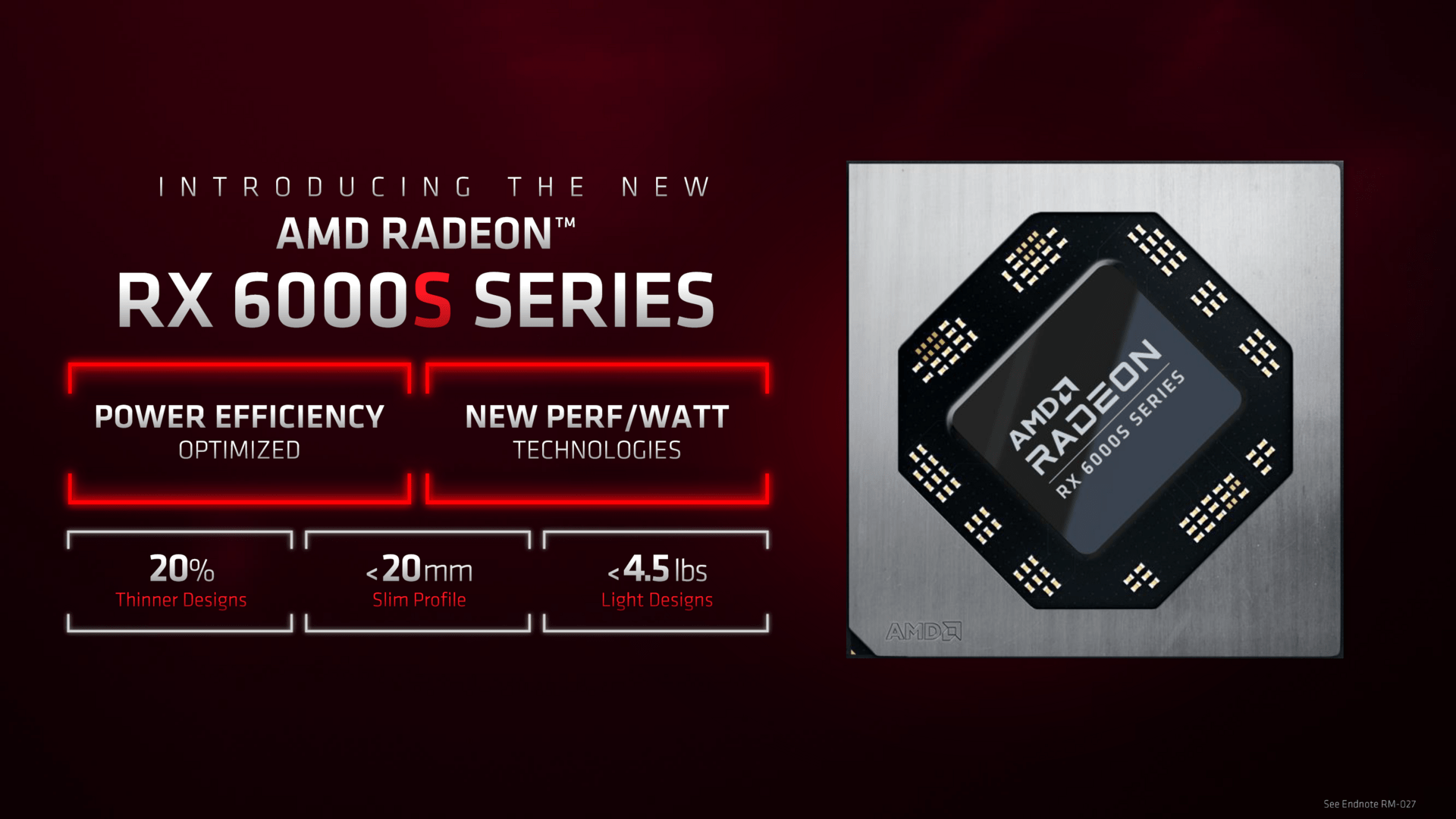
Radeon RX 6000S for “maximum efficiency”
All three S models Radeon RX 6800S, Radeon RX 6700S and Radeon RX 6600S are brand new. “S” stands for slim and is intended to clarify its application area: particularly slim gaming notebooks. Consequently, the S-SKUs are designed for the highest possible efficiency, but have little in common with the respective M variants.
The Radeon RX 6800S corresponds more to a Radeon RX 6650M XT (both Navi 23, both 32 CU, both 8 GB memory) than to a Radeon RX 6800M (Navi 22, 40 CU, 12 GB memory). Thanks to up to 20 watts more power consumption and higher clock rates, the Radeon RX 6650M XT is even faster on paper. It couldn’t be more confusing.
Radeon RX 6800S vs. Radeon RX 6800M
In the end, AMD’s (and Nvidia’s) naming approach is just one class lower: the Radeon RX 6800M has little to do with the Radeon RX 6800, but it is the top of the M-series laptop. And the Radeon RX 6800S has little in common with the Radeon RX 6800M, but it is the top model in the S line particularly efficient on the notebook.
The ratio of RX 6700S to RX 6700M is similar – this GPU is not based on the Navi 22 GPU (cut to 32 CUs) like the RX 6700M, but switches to Navi 23 with 28 CUs, which includes less infinite cache, wide of memory band and storage. When comparing the Radeon RX 6600S to the Radeon RX 6600M, it’s mainly the 4GB memory maximum that makes the difference; otherwise, the maximum settings of both graphics chips are very similar.
The following editors have measured in detail the speed of the Radeon RX 6800S with GPU Navi 23 compared to the Radeon RX 6800M with GPU Navi 22.
This is how the GPUs work in Asus test models
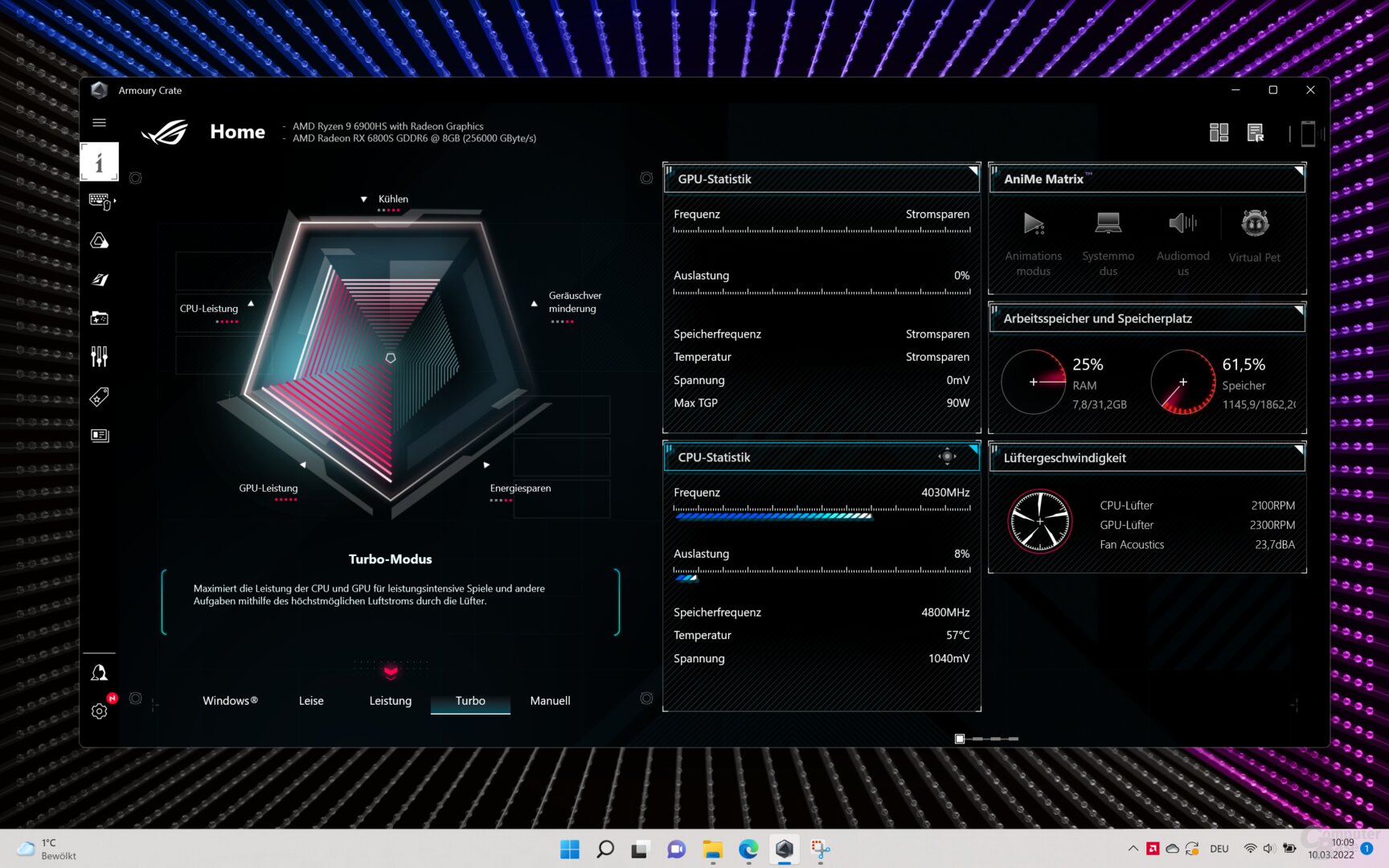
The Asus ROG Zephyrus G14 was once again available for editors to test the Radeon RX 6800S. The same laptop was used to test the Radeon 680M iGPU and the Ryzen 9 6900HS. The Radeon RX 6800M was tested on the Asus ROG Strix G15 2021 with Ryzen 9 5900HX.


dGPU performance tested in turbo profile, as defined by Asus Armory Crate software
For the Radeon RX 6800S in the G14, this means: The GPU can consume up to 105 watts, as long as the temperature of the GPU and the electrical power required by the CPU allow it. In the case of the Radeon RX 6800M, it is much higher up to 179 watts, the influencing factors are the same.
As the diagrams below show, the Radeon RX 6800S in the G14 and the Radeon RX 6800M in the G15 behave very differently within the set parameters. The Radeon RX 6800M shows no negative influence of temperature on performance, power consumption is very constant at 150 watts in FHD and 165 watts in UHD.
The Radeon RX 6800S, on the other hand, only allows itself the maximum allowed 105 watts at the start at both resolutions and runs the highest clock this way. After that, it drops back to the configured minimum of 80 watts at both resolutions, which also results in around 350 MHz underclock.
The decisive influencing factor here does not seem to be the power consumption of the CPU, but rather the temperature of the hot spot of the GPU, which is kept at 100 °C in both tests.
With the exception of F1 2020/2021, this drop in performance is already included in the benchmarks on the following pages, because the other benchmarks were not created from a rest phase, but from a load phase . Only with F1, the benchmark starts directly after loading from the desktop.

Introvert. Beer guru. Communicator. Travel fanatic. Web advocate. Certified alcohol geek. Tv buff. Subtly charming internet aficionado.