Are you afraid of Ethereum 2? – Ethereum is on the way to one of the most important updates in its history with the deployment of its version 2.0. However, the transition from proof of work (PoW) to proof of stake (PoS) will not be a risk-free process. Investigators assess the situation.
Ethereum’s Big Update
Network Ethereum, as we know it, ensures the functioning of its consensus through a mechanism of work test, similar to Bitcoin. However, since its launch, the developers, including the co-founder Vitalik Buterin, I have identified limits to this model. Thus, starting in 2016, the Ethereum developer community plans a proof-of-work transition. You will see the proof of participation.

Since then, things have changed a lot. After several years of development, the move to PoS has never been so close. In practice, this is planned by the developers for the first quarter 2022. Unfortunately, some researchers are starting to point fingers at this transition by highlighting multiple attack vectors.
Ethereum 2.0: proof of stake at risk?
October 19 Caspar Schwarz-Schilling, Barnabé Monnot, Aditya Asgaonkar from the Ethereum Foundation, Joachim new, Ertem Nusret Tas and David Tse from Stanford University have published a scientific article titled “Three Proof-of-Stake Ethereum Attacks”.
As the name suggests, this post highlights 3 attack vectors that could put Ethereum 2.0 in jeopardy.
An attack reorganize
The first attack vector would allow a reorganization attack to be carried out, without necessarily having significant resources.
« The strategy shows that a block proponent who controls a single committee member in the same space can successfully perform a chain reorganization. “
Publication
This attack would take place in 4 steps :
- At the beginning of a slot n + 1, the attacker would create a block privately based on the previous block n. Since the block is private, honest validators would not see it and would attest that the head of the chain is block n;
- At the beginning of the next slot (n + 2), an honest validator would suggest a block n + 2. At the same time, the attacker would publish his private block and vouch for it for space n + 2. Hence, the 2 blocks would be in conflict, because they would share the same parent block;
- As the attacker’s block would have its certificate and would have more weight due to its precedence, honest validators would consider it as the head of the chain;
- At the beginning of slot n + 3, a new honest validator would propose a block n + 3, pointing to block n + 1 as the parent (the attacker’s). This would orphan block n + 2, leading to the attack reorganize in its conclusion.
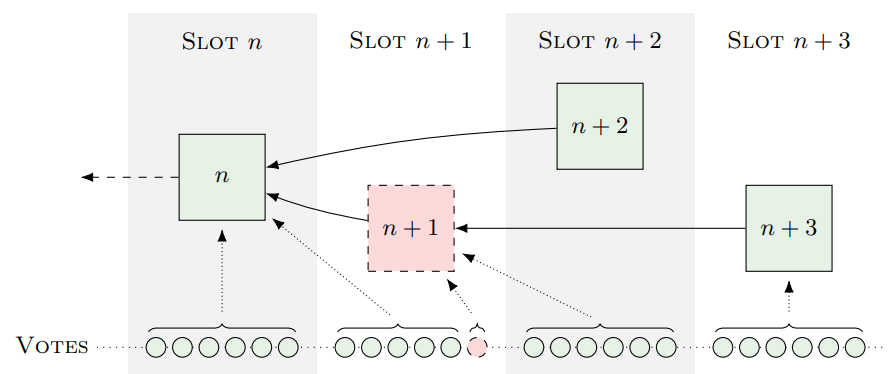
Anyway, keep in mind that this entire attack can only be carried out if the network has no latency, which is highly unlikely. The document concludes that it is a “Non-trivial problem, but achievable in practice”.
Unfortunately, all the actions described above would not be not considered like fraudulent and therefore would not lead to no penalty (slash), unleashing the attacker to repeat as many times as he wants to complete it.
>> Play it safe by investing in benchmark cryptocurrencies with Swissborg <
A balancing attack
The second attack vector identified is a so-called Balance. The goal of this is lock the consensus mechanism d’Ethereum 2.0.
In practice, this attack has 2 main stages:
- Malicious block proponents would propose 2 competing channels, baptized Left and Right;
- Proponents would vote maliciously for the 2 chains in order to guide the vote of honest validators. Attackers will make sure to maintain a equality between the 2 channels to maintain system level and block consensus.
How the validators would not arrive disagree on which channel to choose, the consensus will be locked until it is resolved.
Again, this attack requires preparation and perfect timing. While it is possible in practice, it does not say that it is possible to achieve it in real conditions, with the several thousand validators on the network.
Again, these actions would not be sanctioned by the network. This again leaves the attacker free to persevere until the attack takes hold.
A combination of the first 2 attacks.
The last attack would be to combine the 2 attacks presented above.
“By combining the ideas of these two attacks, we now describe an attack in which the opponent can execute a long-range reorganization with infinitely low stakes and no network delay control. “
Publication
Fortunately, this post arrived several months before the transition to Proof of Stake. Therefore, developers can now take these risks into account, why not publish a new fork that would provide solutions to mitigate the risk of attacks.
Recently, the Ethereum 2.0 network experienced its first fork with the rollout of the Altair update. The first of a long series, this could well be followed by another, following the revelations of this publication.
Contrary to appearances, the Bitcoin and cryptocurrency train is still at the station and waiting for you! Get ready to embark with Swissborg offering you 100 euros in cryptocurrenciess for any new record. (affiliate link, for a minimum deposit of € 50)

Introvert. Beer guru. Communicator. Travel fanatic. Web advocate. Certified alcohol geek. Tv buff. Subtly charming internet aficionado.
